PREVENTING TEEN DATING VIOLENCE
TDV is prevented when teens, families, organizations, and communities work together to implement effective prevention strategies.[14]
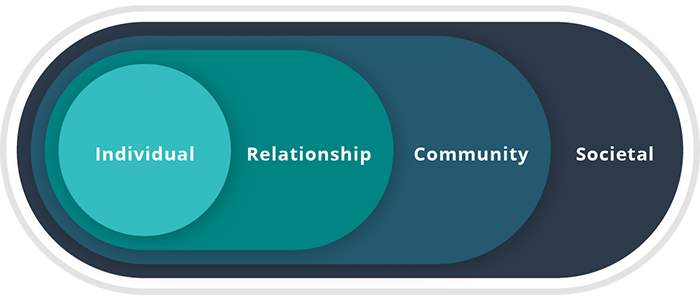
SOCIAL ECOLOGICAL MODEL
Preventing TDV requires a comprehensive approach involving diverse partnerships, working across multiple levels of the social ecological model, to influence the norms and behaviors of individuals, families, peer groups, schools, community and government organizations, neighborhoods, and the society at large (see figure above).[15] Organizations can also work with stakeholders to identify common goals or develop synergy around complementary issues (e.g., parent-child relationship quality, sexual health, substance abuse, Title IX, youth violence, academic achievement, social/emotional learning objectives, and exposure to violence).
EVIDENCE-BASED PROGRAMS
The Dating Matters initiative’s comprehensive approach to TDV prevention includes a range of preventive strategies, including youth and parent education and skill-development programs, educator training, communication strategies, policy strategies, and evaluation and surveillance for individuals, peers, families, schools, and neighborhoods.[16] Evidence-based TDV prevention programs are in use throughout the country and organizations can educate key stakeholders about these programs. The table below provides a list of some evidence-based TDV prevention programs.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has developed Resources for Action to help states and communities take advantage of the best available evidence to prevent violence.
The technical package has three components. The first component is the strategy or the preventive direction or actions to achieve the goal of preventing violence. The second component is the approach. The approach includes the specific ways to advance the strategy. This can be accomplished through programs, policies, and practices. The evidence for each of the approaches in preventing violence or its associated risk factors is included as the third component. This package is intended as a resource to guide and inform prevention decision-making in communities and states.
This Guide and website are provided for informational purposes only. Note that certain restrictions apply to the use of CDC funds for impermissible lobbying. For more information concerning such restrictions see the CDC Anti-Lobbying Guidelines.

